Imaging
The imaging work-up of a child with hepatomegaly, an abdominal mass, or abdominal distension usually starts with abdominal radiography and US.
- Radiography - show hepatomegaly and a nonspecific mass effect in the upper abdomen with displacement of intestinal structures, as well as occasional calcifications within the projection of the liver or mass
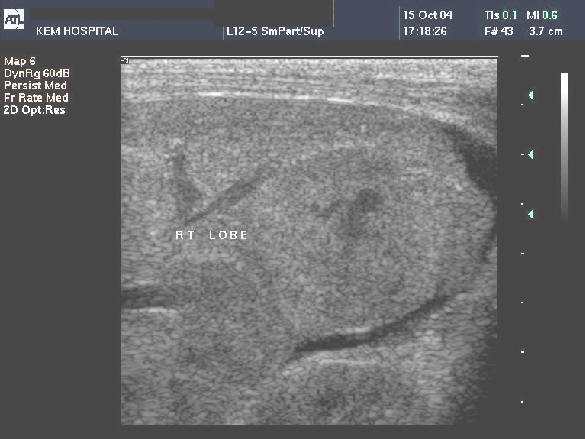
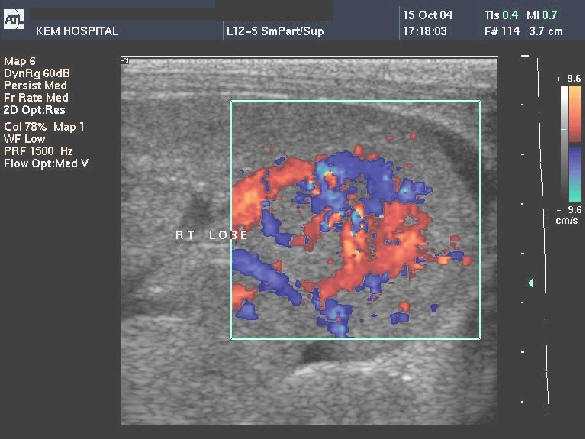
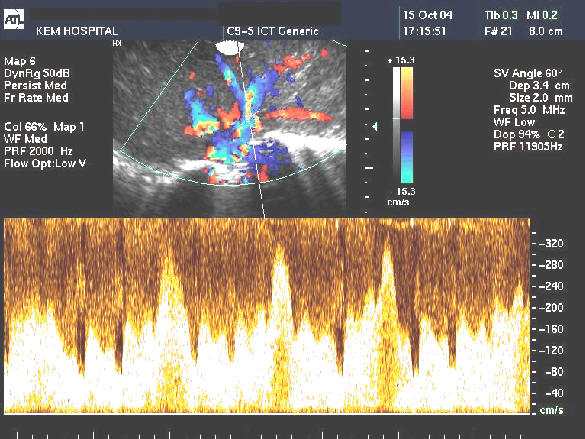
- USG - infantile hemangioendothelioma appears as a complex, mostly solid hepatic lesion with variable hypo and hyperechoic echotexture. In cases of significant arteriovenous shunting, dilated hepatic vasculature with prominent blood flow at Doppler US is typical. If large vascular spaces are present, anechoic regions with detect-able flow may be seen . The lesions are often well demarcated from the surrounding liver parenchyma.
Epidemiology
Hepatic tumors in children are relatively uncommon (about 2%–3% of all pediatric tumors). However, infantile hemangioendothelioma is the third most common hepatic tumor in children (12% of all childhood hepatic tumors), the most common benign vascular tumor of the liver in infancy, and the most common symptomatic liver tumor during the first 6 months of life.
Clinical Features
The tumor may be asymptomatic and discovered incidentally. More often, however, the tumor is large and manifests as hepatomegaly, abdominal distention, or a pal-pable upper abdominal mass. There may be ex-tensive arteriovenous shunting within the lesion, resulting in decreased peripheral vascular resis-tance. Thus, increased blood volume and cardiac output are required to maintain vascular bed per-fusion, which may lead to high cardiac output and congestive heart failure in up to 50%–60% of pa-tients
Differential
The most important alternative diagnosis to infantile hemangioendothelioma in this age group is hepatoblastoma
The most important alternative diagnosis to infantile hemangioendothelioma in this age group is hepatoblastoma