CREUTZFELD JACOB DISEASE
Def - Rapidly progressing, fatal potentially transmissible disorder caused by prions (proteinaceous particle devoid of DNA and RNA).
Other prion diseases include Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome (GSS), fatal familial insomnia (FFI) and kuru in humans.
People can also acquire CJD genetically through a mutation of a gene (needs to be defined). This only occurs in 5-10% of all CJD cases.
The CJD prion is dangerous because it promotes refolding of native proteins into the diseased state. The number of misfolded protein molecules will increase exponentially and the process leads to a large quantity of insoluble prions in affected cells. This mass of misfolded proteins disrupts cell function and causes cell death.
Incidence and prevalance –
1)Although CJD is the most common human prion disease, it is still rare and only occurs in about one out of every one million people.
2) It usually affects people aged 45–75, most commonly appearing in people between the ages of 60–65.
3) The exception to this is the more recently-recognised 'variant' CJD (vCJD), which occurs in younger people.
1)Although CJD is the most common human prion disease, it is still rare and only occurs in about one out of every one million people.
2) It usually affects people aged 45–75, most commonly appearing in people between the ages of 60–65.
3) The exception to this is the more recently-recognised 'variant' CJD (vCJD), which occurs in younger people.
Symptoms –
1)rapidly progressive dementia leading to memory loss.
2) personality changes and hallucinations.
3)speech impairment,
1)rapidly progressive dementia leading to memory loss.
2) personality changes and hallucinations.
3)speech impairment,
4)jerky movements (myoclonus).
5) balance and coordination dysfunction (ataxia), changes in gait, rigid posture and seizures.
Clinical and Pathologic Characteristics-
Characteristics Classic CJD Variant CJD
1)Median age at death 68yr 28yrs
2)Median duration of illness 4-5 months 13-14 months
3)Clinical signs and symptoms early neurological signs delayed neurological sign
4)periodic sharp wave on EEG often present often absent.
5)Signal hyper intensity in often present often absent
basal ganglia in flair T2
and diffusion weighted,
6)pulvinar sign on MRI not reported present in 75% cases
7)Immunohistochemical
analysis of brain tissue variable accumulation mark accumulation of
protease resistant protein.
8)present agent in lymphoid not readily detected readily detected.
tissue.
9) Increased glycoform ratio not reported mark accumulation of
on immunoblot analysis of protease resistant protein.
10) Presence of amyloid plaques in may be present may be present
brain tissue.
Imaging findings –
CT finding –
NECT-
Usually show normal (80%) or generalized atrophy of brain , ventricular dilatation in 20%.
MRI finding-
T1W-
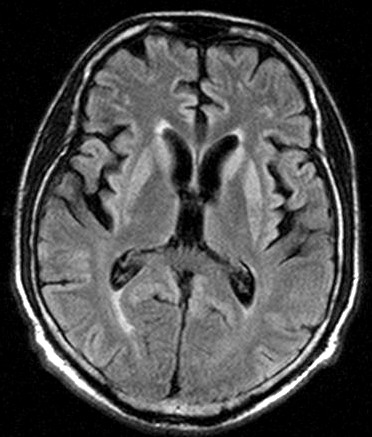
Hyper intensity on T1W in globus pallidus in sporadic cases .
T2W-
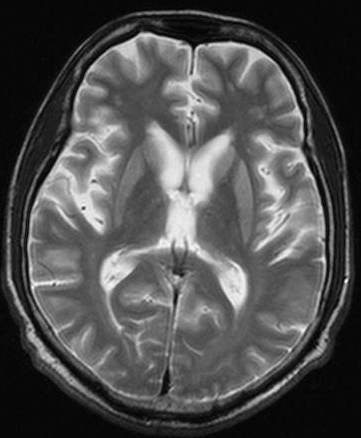
Hyper intense signal in basal ganglia , and thalamus ,
High signal intensity in cortical grey matter ,cerebral atrophy.
FLAIR- Two sign of new varriant CJD
1)Pulvinar signs –bilateral symetrical hyperintensity pulvianr (posterior)
nuclei of thalmus relative to anterior putamen.
2)Hocky stick sign-
symetrical pulvianr, dorsomedial thalamic nuclear hyperintensity
3) Periductal grey matter hyperintensity.
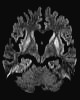
D1W1- Progressive hyper intense changes in straitum and cerebral cortex.
Gyriform hyperintense area on cerebral cortex.
D1W1 hyperintensity may disappers later in disease.
Differential diagnosis-
1) Hypoxic ischamic encephalopathy-
BG and parasaggital cortical area involved Hyperintense BG lesion on T1W1 and
. T2WI.
2) Other causes of dementia-
a)Alzheimer disease.
b)dementia in motor neuron disease.
c) front temporal dementia.
d)multiinfarct dementia.
3) Bilateral T2 hyperintense BG abnormalities –
a) small vessel ischemic disease.
BG involvement , asymmetrical and multifocal, focal hyperintensity in corona
Radiata and centrum semiovale.
b) Wilson disease- WM and deep grey matter involvement, dentate nucleus,BG ,
T1 hypointense lesion ( occasionally hyerintense)
Variable hyperintense/ hypointense/both on T2
c) HIV encephalopathy and AIDS dementia complex-
similar lesion in putamen
d) Leigh disease-
Primarily childhood disease
T1W1 hypointense
e) Cortical basal ganglionic degeration .