SUB ACUTE SCLEROSING PAN ENCEPHALITIS (DAWSON ENCEPHALITIS)
Rare progressive measles virus mediated encephalitis occurring after a clinically silent period of months – years.
Etiology:
Measles virus – mutant form. 16x higher risk of developing SSPE.
Gross pathology: Diffuse swelling, atrophy, cortical petechial bleeds, subcortical encephaloclastic lesions in non-vascular distributions.
Microscopic features: widespread myelin loss, gliosis, diffuse neuronal loss, Alzhimer-like neurofibrillary tangles, diffuse glial neurofibrillary tangles, perivascular lymphocytic cuffing by T and B cells.
Clinical features:
H/O measles infection before 2 years of age.
Presents in childhood, adolescence. Progressive mental deterioration, motor impairment, myoclonus.
Insiduous onset, subacute course, death in 1 – 6 months. Rarely, patients’ clinical features and imaging features improve.
Positive CSF, plasma complement fixation test for measles. CSF oligoclonal bands.
EEG – periodic complexes with generalized polyspikes, increased voltage slow waves every 5 – 10 minutes.
Imaging features:
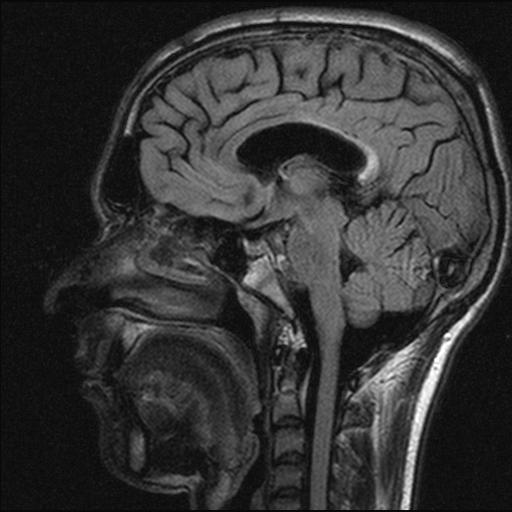
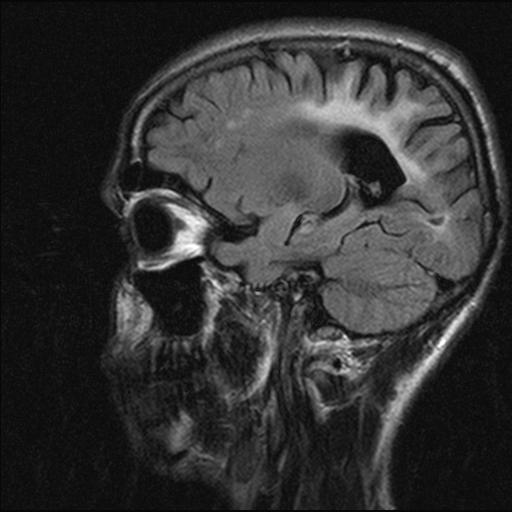
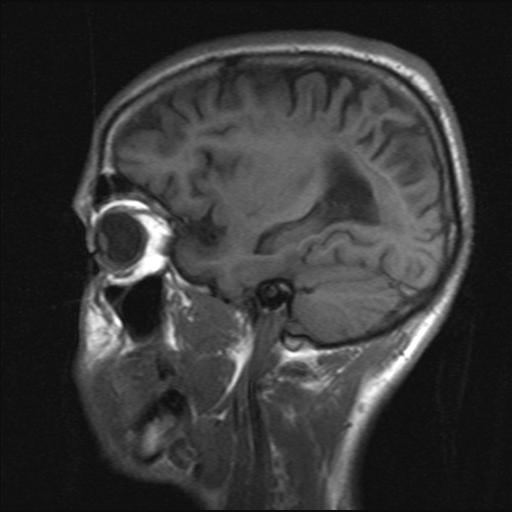
CT – normal in early stages. May show diffuse brain swelling, no focal lesions, low density in white matter. Late stages show atrophy.
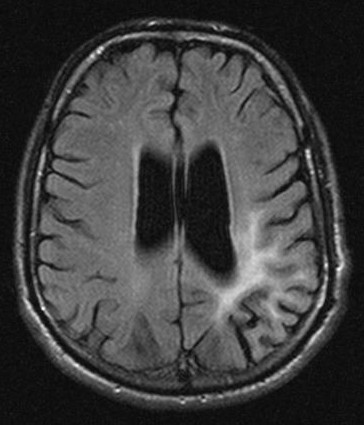
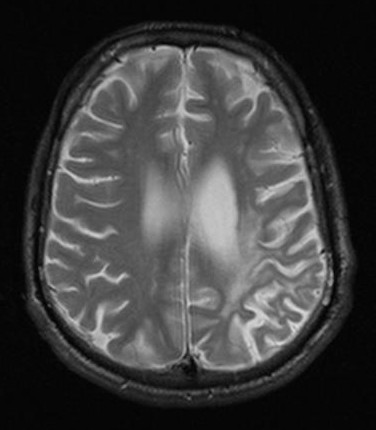
MRI – signal changes are seen in periventricular or subcortical white matter of parietal or occipital lobes.
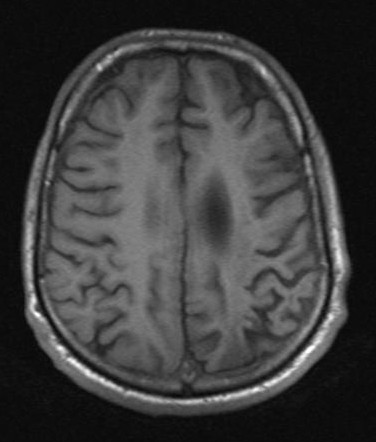
T1WI – decreased signal in white matter or corpus callosum.
T2WI – diffuse increase in signal in white matter or corpus callosum. Symmetric. No mass effect.
Rarely, cystic temporal lobe lesions are seen.
Late stages – diffuse atrophy.
Involvement of basal ganglia / thalami is rare (esp. in adults)
No contrast enhancement.
Differential diagnosis of confluent T2 hyperintense white matter lesions:
ADEM, PML, tumefactive multiple sclerosis, HIV, post infectious measles encephalitis (distinguished by time of onset)